In August 2021, it was reported that Japan are starting to close the gap among the global 5G leaders with four of the main Operators accelerating their 5G roll-out through the expansion of base stations across the country. We had a chat with Shun Miyamoto from Marubun Information and Communication Team to discussing the emerging wireless connectivity developments in Japan.
What wireless network initiatives are you seeing in Japan?
About 4 years ago, the Japanese government launched the Connected Industries strategy to support smart factories. Part of this initiative included the Connected Industries Tax System (IoT Tax System) which provides financial support for installing systems, sensors and robots to improve productivity through machine-to-machine communication.
We have witnessed a significant growth and uptake of local private 5G services in the manufacturing sector, with the creation of smart factories. We are currently working with multiple customers to facilitate the design and implementation of their private wireless networks.
What is a smart factory?
A factory that uses IoT sensors and other technologies to collect data and communicate improvements to machinery processes through automation and self-optimisation. Artificial intelligence (AI) is taking automation to the next level by making complex optimisation decisions that humans typically make. The benefits extend beyond the physical production line into functions like planning, supply and logistics.
What wireless challenges are you facing inside a Smart Factory?
A reliable wireless network connection is required to maintain the seamless production process, and our customers are facing a number of challenges, such as:
- A typical indoor factory environment is filled with machinery made from metal and steel which is not friendly to wireless communications. The metal can reflect or diffract wireless signals making it challenging to plan a network that will cater for these materials.
- The equipment installed in factories often comes with its own wireless connection or Wi-Fi access points and when you install tens or hundreds of machines inside a building, it creates a very densely populated wireless environment which can cause interference and put a strain on the network. Ultimately this can lead to poor performance and potentially production delays.
- Each Smart Factory is laid out differently and with so many technologies available, it can be difficult to determine which components and configurations are best suited for the environment.
How are you enabling 5G in Smart Factories?
Many of our customers are looking to utilise localised private 5G networks because they can provide the dedicated service and capacity needed to ensure reliable machine-to-machine communications. Advances in network slicing and security are also beneficial to allocate the required resources and ensure stability of the network. Though the technology is available, the planning and configuration of the network to function properly in the environment needs careful consideration.
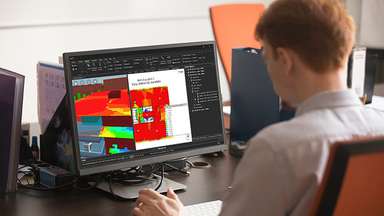
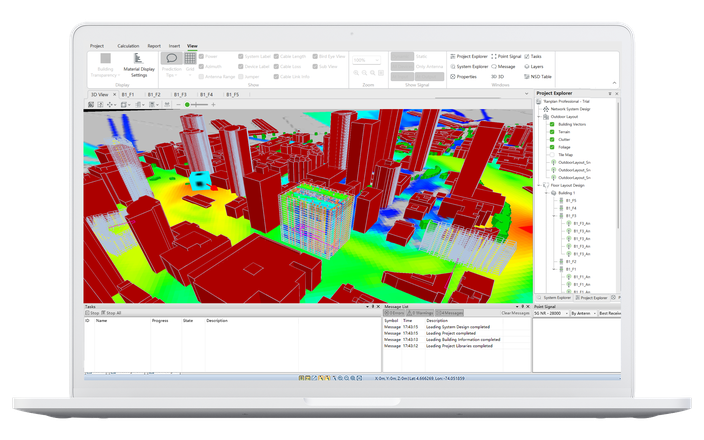
We have several projects utilising the Ranplan Professional Network Planning software. One of which is a proof-of-concept for a 20,000-square-meter smart factory for steel and non-ferrous metal manufacturing conducted by Sumitomo Corporation.
To overcome the challenges of machinery and steel materials affecting the signal propagation, Sumitomo Shoji Machinex, the company responsible for the network design, used Ranplan Professional to model the environment after a thorough site survey. The efficient modelling capability enabled them to model all aspects, including the machinery, and assign material information to accurately replicate the environment before planning the network design.
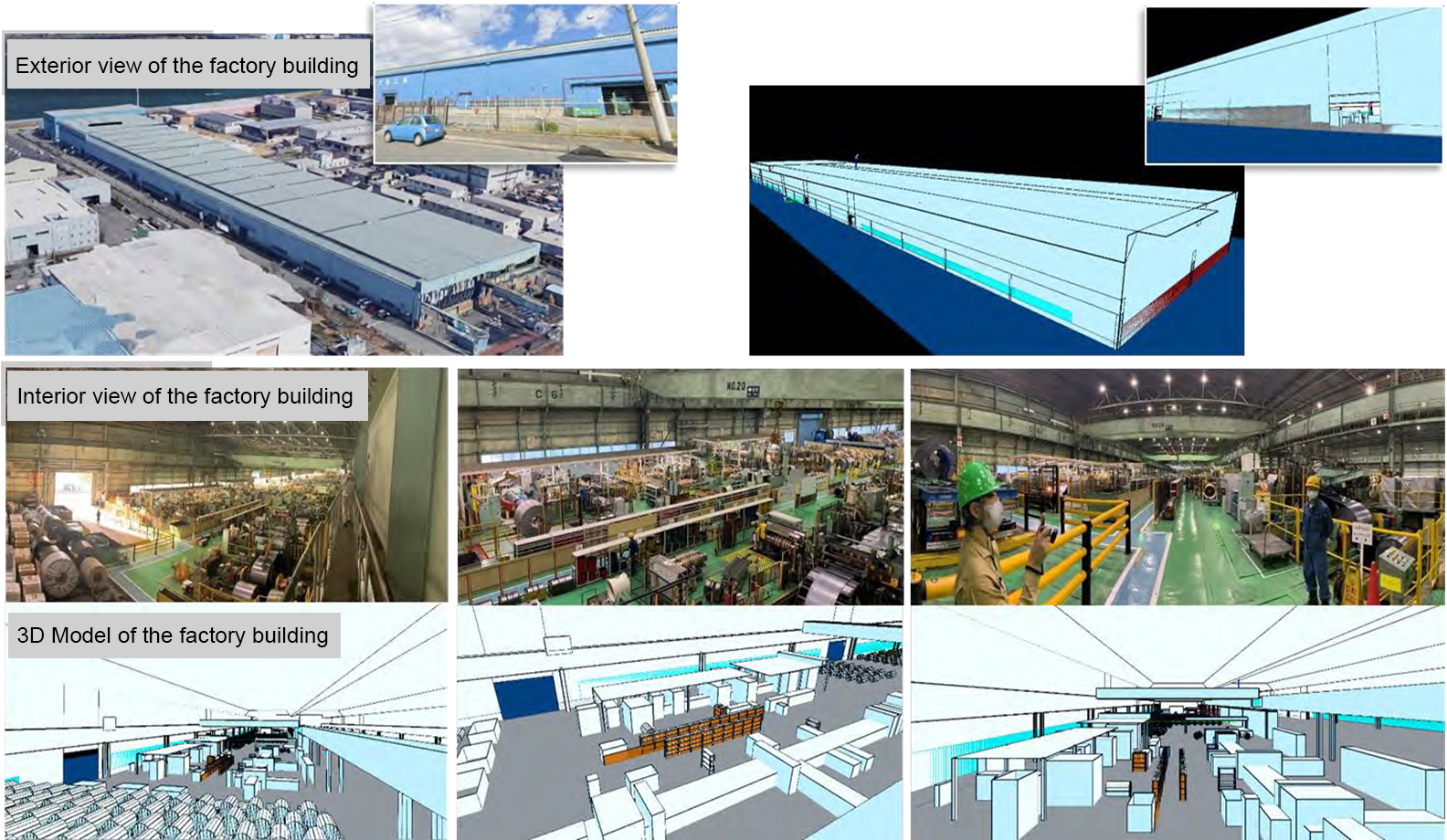 Image: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (latter half) FY2020 L5G Development Demonstration Report_No7\Automating Visual Inspection and Remotely Confirming Quality P136 - link
Image: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (latter half) FY2020 L5G Development Demonstration Report_No7\Automating Visual Inspection and Remotely Confirming Quality P136 - link
With many installation restrictions, the 3D RF propagation simulations played an important role to determine the quantity and location of base stations to deliver the required wireless coverage. Sumitomo Shoji Machinex calibrated the accuracy of the simulations by importing onsite measurement data. The simulations were performed under a variety of conditions such as opened and closed factory shutters to see how this would impact the signal propagation. This helped to investigate the cause of signal loss in certain areas of the building and ascertain the appropriate tilt angle of the antennas to maximise coverage performance and minimise signal leakage.
Outdoor leakage level exceeds -80dBm in some locations
Slight reduction in outdoor leakage above -80dBm compared to tilt 20°.in some locations
Field strength at the UE installation location is 80~90dBm with minimal leakage to the outdoors
Field strength at UE location is less than -90 dBm, with some locations below -110dBm
Images: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (latter half) FY2020 L5G Development Demonstration Report_No7\Automating Visual Inspection and Remotely Confirming Quality- link
The ability to precisely model unique environments and optimise network designs with the use of 3D RF simulations and productivity-enhancing automation tools has delivered and will continue to deliver substantial time and cost savings for our customers.