Staying connected while on the move has become an integral part of modern transportation systems. Whether commuting through tunnels, travelling by train, or waiting in underground stations, passengers expect seamless access to wireless networks for internet connectivity, communication, and entertainment. However, providing reliable wireless connectivity in tunnels presents unique challenges due to factors such as signal attenuation, tunnel geometry, and infrastructure limitations. In this blog, we explore the considerations, planning strategies, and benefits of wireless connectivity in tunnels, along with the role of advanced technologies in addressing these challenges.
Challenges in Tunnel Connectivity
Transportation tunnels, especially railway tunnels, pose significant challenges for wireless connectivity due to their enclosed nature, which can cause signal attenuation and interference. Passengers often experience disruptions or complete loss of network coverage while travelling through tunnels, leading to frustration and inconvenience. Additionally, the diverse characteristics of tunnels, including length, curvature, lining material, and infrastructure constraints, further complicate the deployment of wireless networks.
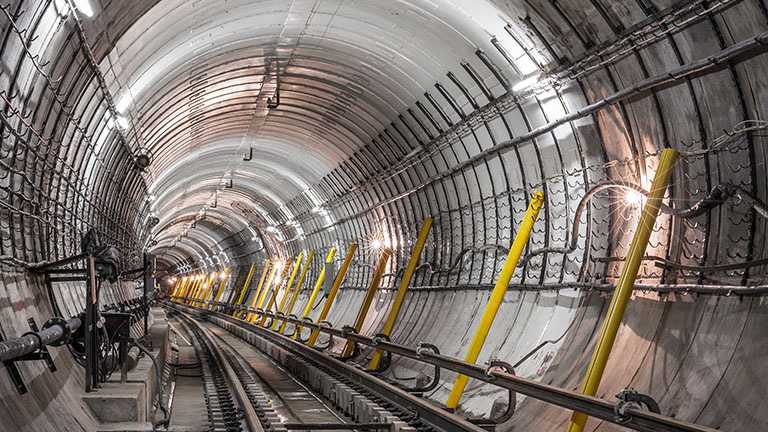

Considerations for Wireless Connectivity
Achieving seamless wireless connectivity in tunnels requires careful consideration of various factors, including:
- Tunnel Characteristics: Each tunnel has unique characteristics, such as length, curvature, and lining material, which influence signal propagation and coverage. Understanding these characteristics is essential for designing effective wireless networks.
- Signal Propagation: Wireless signals behave differently in tunnel environments than open spaces. Factors such as tunnel curvature, lining material, and obstructions affect signal propagation, requiring tailored solutions for optimal coverage.
- Data Link Options: Depending on the infrastructure and passenger requirements, wireless connectivity can be provided through direct access to mobile network operators (MNOs) or intermediate data links via on-train gateways and antennas. Each approach has its advantages and challenges, requiring careful planning.
- Technology Selection: Current and emerging technologies, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and millimetre-wave (mmWave), offer different capabilities for tunnel connectivity. Selecting the most suitable technology depends on factors such as frequency band, capacity, installation and compatibility with existing infrastructure.
- Capacity Planning: Estimating the demand for data throughput and capacity within tunnels is crucial for designing robust wireless networks. Factors such as passenger traffic levels, device usage, and data services influence capacity requirements and network performance.
Planning Strategies and Solutions
To address the challenges of wireless connectivity in tunnels, transportation authorities and network planners can adopt various planning strategies and deploy innovative solutions:
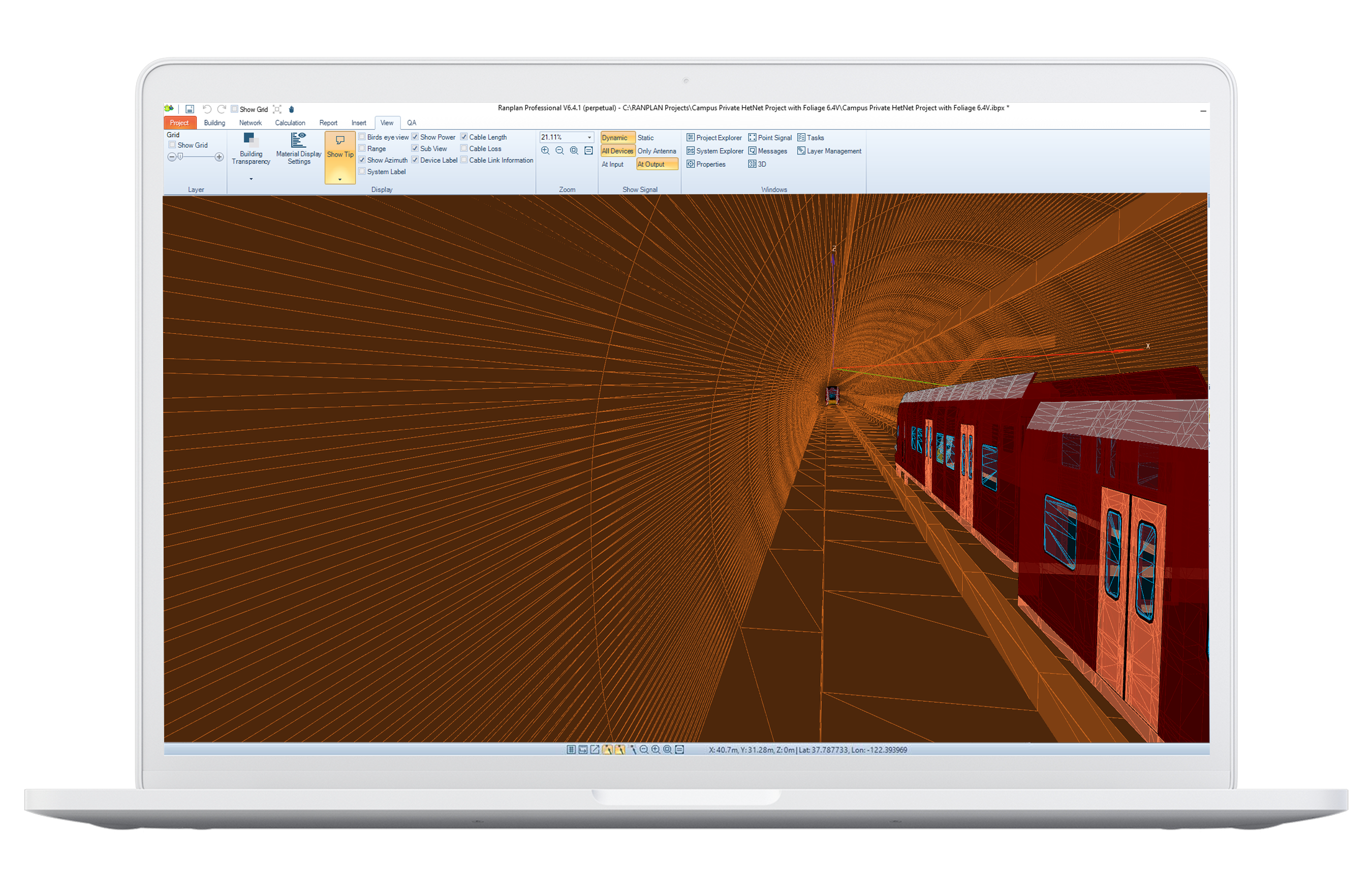
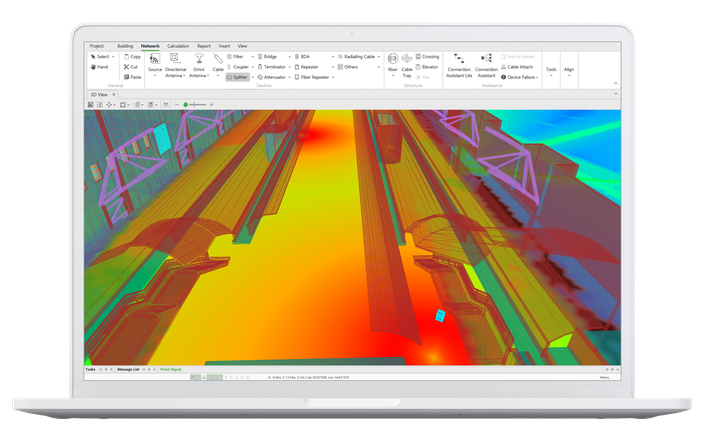
- Advanced Network Planning Software: Utilising specialized software tools, such as Ranplan's network planning software (Ranplan Professional), enables accurate modelling and simulation of tunnel environments. These tools facilitate the design and optimization of wireless networks tailored to specific tunnel characteristics and requirements.
- Advanced 3D Tunnel Modelling: Incorporating advanced 3D modelling capabilities enables planners to simulate real-world scenarios with precise representations of tunnels, trains, and infrastructure. These tools capture detailed information about tunnel geometry, including horizontal and vertical profiling, cross sections, and construction materials. By leveraging this level of granularity, planners can accurately predict signal propagation and coverage, leading to optimized network designs and ensuring reliable performance.
- Intelligent Automation: Leveraging intelligent automation modules streamlines the network design process, saving time and resources while optimizing network performance. Automation tools assist in tasks such as device selection, configuration, and parameter optimization, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Signal Propagation Simulations: Advanced simulations using 3D ray-tracing techniques provide insights into signal coverage, capacity, and quality of service. Planners can analyse various scenarios, assess potential interference, and fine-tune network parameters to meet performance targets.
Benefits of Enhanced Connectivity
Deploying robust wireless connectivity in tunnels offers numerous benefits for passengers, transportation operators, and infrastructure providers:
- Improved Passenger Experience: Seamless connectivity enables passengers to stay connected, access information, and enjoy entertainment during their journey, enhancing overall satisfaction and comfort.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Real-time communication and surveillance capabilities support safety and security measures, facilitating emergency response, incident management, and risk mitigation.
- Operational Efficiency: Wireless connectivity enables efficient operations, including ticketing, scheduling, fleet management, and maintenance. Automation and data-driven insights optimize resource utilization, reduce downtime, and improve service reliability.
- Integrated Transportation Systems: Seamless connectivity fosters integration between various transportation modes and infrastructure elements, leading to smarter, more interconnected transportation networks.
Planning the Way for Smarter, Safer, and Seamless Transportation Networks
Wireless connectivity plays a vital role in enhancing transportation systems, especially in tunnels where traditional network deployment faces significant challenges. By understanding the unique characteristics of tunnels, adopting advanced planning strategies, and leveraging innovative technologies, transportation authorities can provide seamless connectivity to passengers while realizing operational efficiencies and safety enhancements. With the right approach and tools, tunnels can become seamless extensions of interconnected transportation networks, enriching the travel experience for millions of commuters worldwide.