Resetting expectations and operations
Following a tumultuous 2023, which saw a drastic decline in network spending due to soaring costs of capital, providers of wireless products and services are actively taking steps to adjust their operations to a more tempered investment climate. The downsizing over the last 12 months has seemed almost as prevalent as during the meltdown at the turn of the millennium. Given the lagging effects of rising interest rates, recent declines in leading economic indicators and an air of heightened risk aversion, the prospect of an imminent upturn in 2024 seems unlikely. Even so, history suggests that recoveries from prevailing levels - propelled by pent-up demand following extended periods of minimized spending to barely maintain existing infrastructure – tend to be swift and substantial. Notably, potential catalysts for this revitalization emanate from the release of new spectral resources, support for mid-band deployments and the introduction of 5G advanced (enabling advanced use cases with emphasis on elevated network efficiency and performance). These developments present promising avenues for the industry's adaptation and growth in the foreseeable future.
Generative AI and Cognitive Computing come of age
Of all the technology levers, nothing compares with generative artificial intelligence (AI) – heralding leaps in the ability of software algorithms to mimic and understand human minds, interpret and respond to text, sound and (moving) pictures, and, perhaps above all, automate virtually all cognitive processes (traditionally) carried out by our brains. AI is poised to transform the developments and operations of IT and Telecommunications networks. By synthesizing copious amounts of data - far beyond what any human being can handle - Cognitive Computing (a term that arguably encapsulates this field better than Artificial Intelligence) will be able to draw inferences and make conclusions more accurately and faster than known today. An unmissable pre-requisite, invariably, is how well the underlying software code is trained – whether the feedback is automated or manual, the learning process is critical to obtaining the wanted outcome. In 2024, the industry is likely to witness a surge in innovations, driven by the acceleration of these capabilities.
O-RAN springs back to life
The ups and downs of the O-RAN community have been regularly featured in sector news on almost a daily basis. Doubts have been cast about its future amid a series of high-profile departures, technical obstacles and a slow pace of standardization. However, recent developments should lessen concerns and signal a potential shift in the right direction. AT&T’s eye-opening commitment - over $14 billion allocated to an ambitious 5-year 5G network modernization program with Ericsson appointed the chief (sole) architect – marks a significant turning point. This spectacular move, which brings the top tier vendor into the realm of O-RAN, may be viewed as contradictory, considering O-RAN’s origins in mixing best-of-breed hardware and software from multiple vendors. Nevertheless, it demonstrates what is needed to establish an industry template in motion. It tacitly illustrates the cost and complexity of system integration and supplier coordination – by opting for a single-vendor (Ericsson) initial solution, AT&T at least removes these quandaries (there is one point of responsibility for the whole network).

Granted, the pivotal question lingers: How open will O-RAN truly be?
Its future impact on radio networks, the supplier ecosystem, and the involvement of government agencies in many parts of the world, make it a closely monitored space over the next 12 months. This scrutiny extends to initiatives like the GSMA Open Gateway which stole much of the limelight during the inauguration of the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona 2023. All eyes are now centered on whether the wireless industry’s collective effort will come together to define a minimum set of requisite Application Programmable Interfaces (APIs), enabling universal access to (almost) all service providers’ networks – a crucial step towards monetizing investments by enhancing connectivity with critical functionalities."
Connectivity with Functionality
For all the frenzy surrounding 5G during its incipient years, the latest generation of cellular technologies has yet to live up to its hype. Deployments to date have principally been confined to building out coverage in the low band. Concepts like beamforming, network slicing and stand-alone 5G have proven to be far more intricate than ever anticipated. So far, 5G can be best characterized as an extension of 4G, delivering tangible efficiency gains and general performance enhancements but not to the degree of unleashing the swathe of new applications upon which the initial expectations were formed – the vast majority of which necessitate entirely new 4G/5G-powered indoor networks. However, critical lessons have been learnt.
In the era of GSM, networks were designed and constructed to cope with statistically quite predictable traffic patterns for a single service - voice (plus some text). Today, the situation is markedly different - a 4G/5G network initially built to cater for the projected demands in a shopping mall will invariably need continual refinement and optimization. Their ability to dynamically allocate resources (preferably in near real-time) based on commercial value and critical needs is paramount. In times of inordinate loads, they must be capable of ‘self-repairing’ should serious connectivity issues arise. What remains certain is that capacity needs will soar, and predictability, reliability and security are indispensable elements to enable the most advanced of applications.
Predictability, Reliability and Security for Private Wireless
Establishing lasting interest in private wireless – the premium segment requiring premium quality of service – must involve more attention being paid to predictability, reliability and security tailored to each specific use case. A deep understanding of processes and workflows as well as wireless network engineering are central to producing the results that the inter alia manufacturing, mining and utility sectors demand. In some situations (think drones and robotics in a pure indoor setting) redundancy and ultra-low latency are imperative. In other environments, more akin to a Campus such as an airport, stadium or train station, the mitigation of interference between the public and the private domains will be crucial to the effective re-use of precious spectrum. These remarks notwithstanding, there is no doubt that 5G networks – perfected to meet customer specific requirements – have the qualities to engender tremendous value for industry and society at large. Asset tracking, remote surveillance, machine control and quality inspection are merely a few examples of fields where wireless connectivity armed with proper functionality stands to generate transformative change for the better in coming years. The foundational blocks to this journey ought to become more visible in 2024.
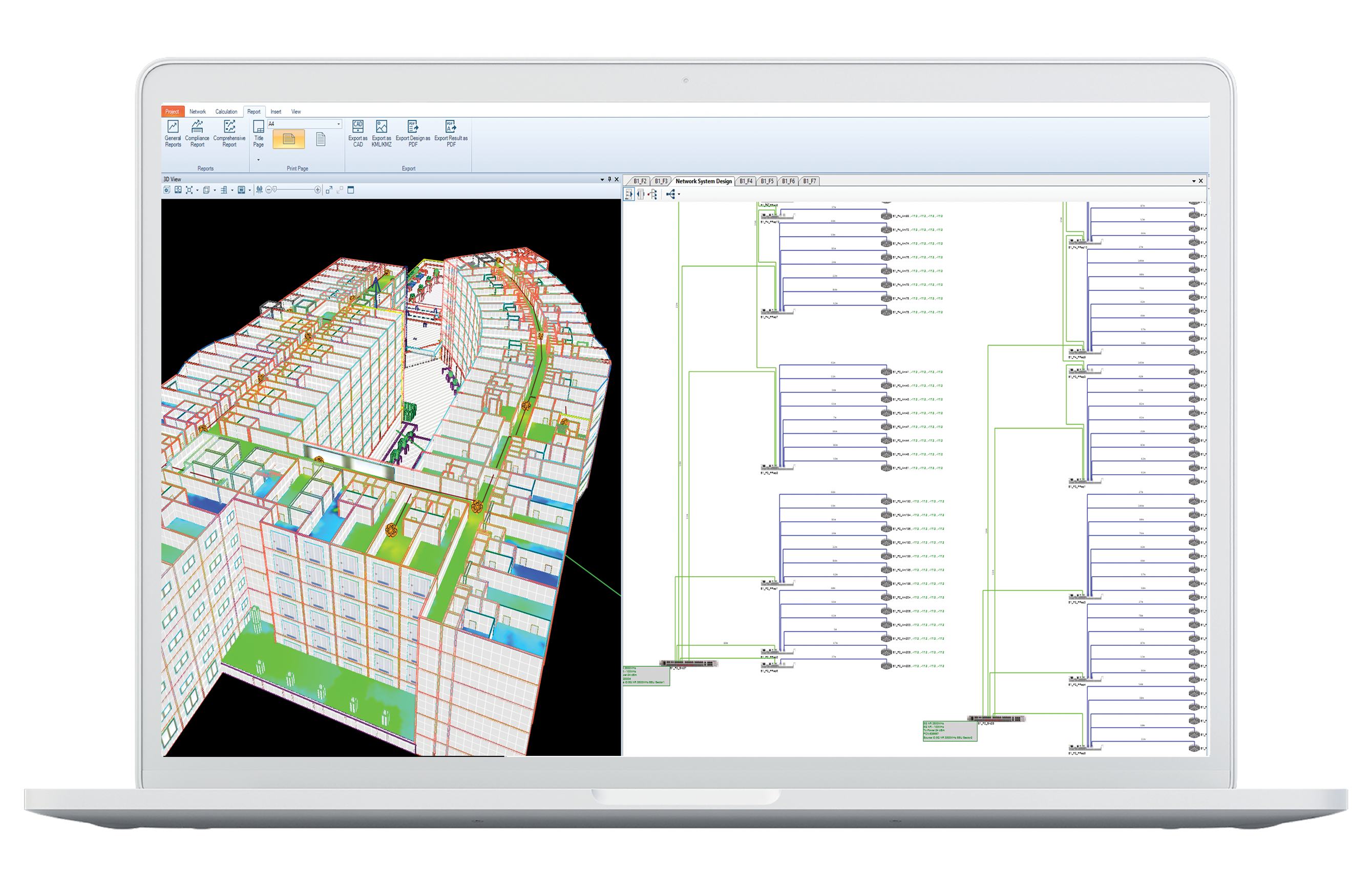
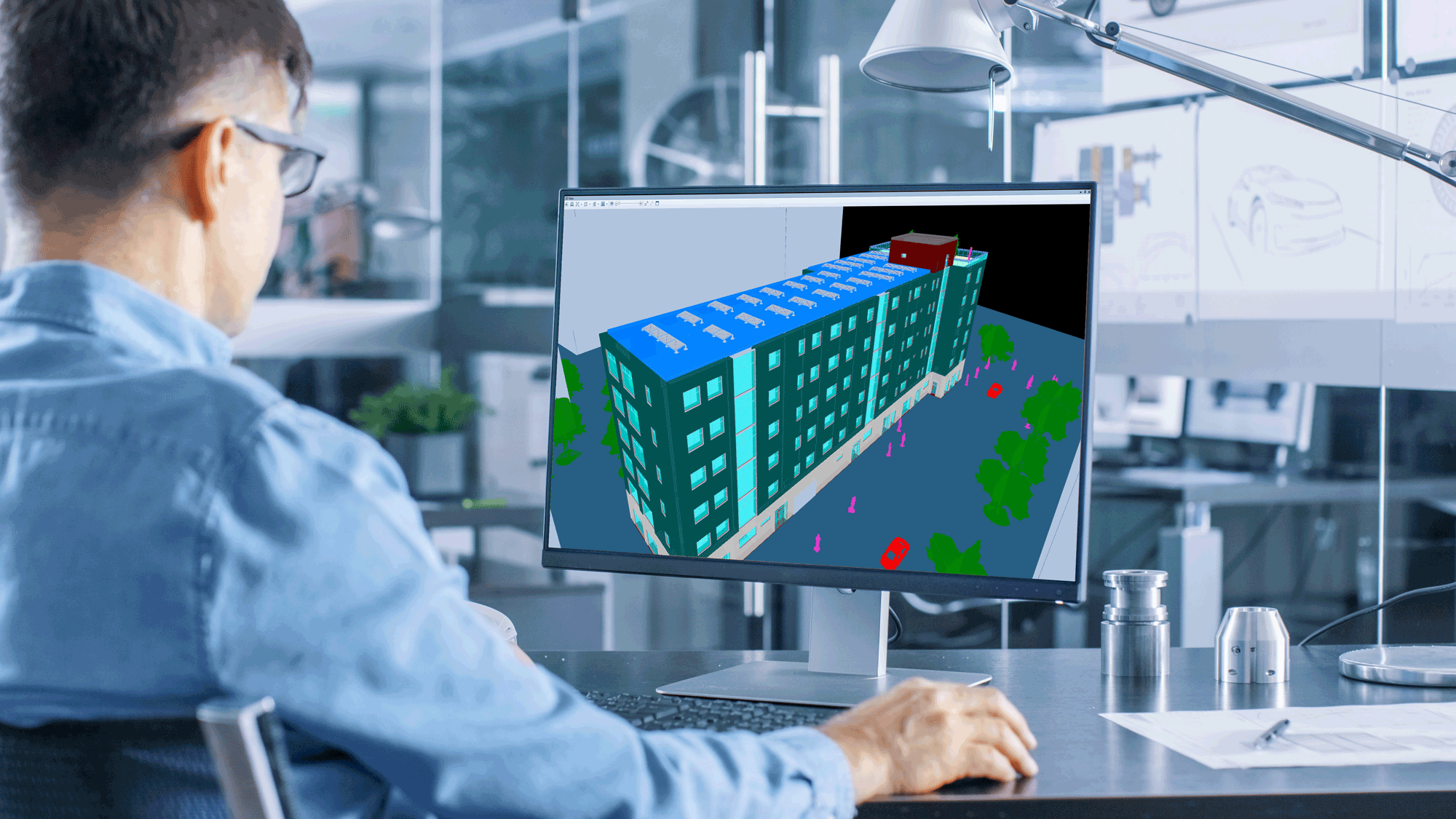 Example of result from IFC import into Ranplan Professional
Example of result from IFC import into Ranplan Professional
Open File Formats in the spirit of BIM
The ability to simulate the performance and resilience of telecommunication networks will become increasingly pivotal to ascertaining that pre-set requirements are met. Given the sheer diversity of use cases and the variety of situations to be addressed, the benefits of standardising Digital Representations (also known as Digital Twins) of the environment and communication networks are more compelling than ever. Open file formats in the spirit of BIM (Building Information Modelling) are pivotal to ensuring easy exchange and re-use of data between different software components. It promises to radically reduce burdens associated with system integration and supplier coordination, enhance the user experience, shorten time-to-market of innovations and slash life-cycle costs on both the CAPEX and OPEX fronts. By the end of 2024, we foresee that notable advances will be recorded on this scene with a few front-runners showing in practice how interoperable architectures can be developed.
 Energy-efficiency to tackle climate change
Energy-efficiency to tackle climate change
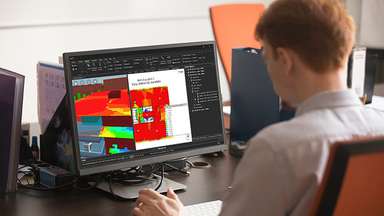
While the fear of an imminent electricity crunch has lessened from the situation a year ago, energy-efficiency will stay at the top of corporate and government agendas for the foreseeable future. The growing reliance on increasingly power-consumptive computers and networks in the era of generative AI, 5G/6G and Digital Twins will put the spotlight on the role of ICT in containing or at least mitigating the effects of global warming. Incentives to modernize equipment, accelerate the shift from 4G to 5G, carefully design new networks or optimize existing ones become ever more compelling. With the help of beamforming, network slicing, smart repeaters (Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces) and a host of AI-inspired technologies, material performance advances and cost savings can be achieved concurrently.
The common denominator, as heralded by the popularity of cloud-centric services, is software which guides and instructs hardware resources to adapt their work in time and space. Just as state subsidies have effectively supported the construction of wind-farms, solar-plants and green-steel factories (as well as the removal of highly diesel/gasoline consumptive vehicles), these incentives can be used to spur telecom operators – historically frustrated by painfully poor returns on investments – to reduce their implied ‘carbon footprint’. This reduction can be achieved by accelerating the replacement of existing infrastructure with the latest eco-friendly technologies, in line with global sustainability objectives.

Ranplan in 2024
In the upcoming year, Ranplan is committed to pioneering advancements across multiple fronts in the wireless network planning landscape. Here are a few areas we envisage our support will influence the wireless industry in 2024:
- Our seamless IFC file imports from BIM authoring software will streamline and enhance the network planning precision while creating significant time and cost efficiencies. Find out more
- Our efforts in energy consumption planning stand at the forefront, driving initiatives to create sustainable, energy-efficient networks that align with global environmental goals. Find out more
- Our focus on private wireless planning signifies our dedication to empowering industries with tailored, top-tier wireless network designs, addressing diverse needs such as ultra-low latency and high reliability. Find out more
- Finally, the expansion of our design and migration services aims to ease the burden of creating intricate new network designs or transitioning from previous software. Our goal is to provide seamlessly optimized network designs ready for deployment. Find out more
Through these concerted efforts, Ranplan remains committed to shaping the future of telecommunications by fostering innovation, sustainability, and unparalleled network excellence in 2024 and beyond.