- However, it faces several technical challenges (TCs):
- The deployment of WNDT in 5G/6G use cases (e.g., last-mile smart logistics) faces huge challenges, as the key components and key performance indicators (KPI) are largely un-known.
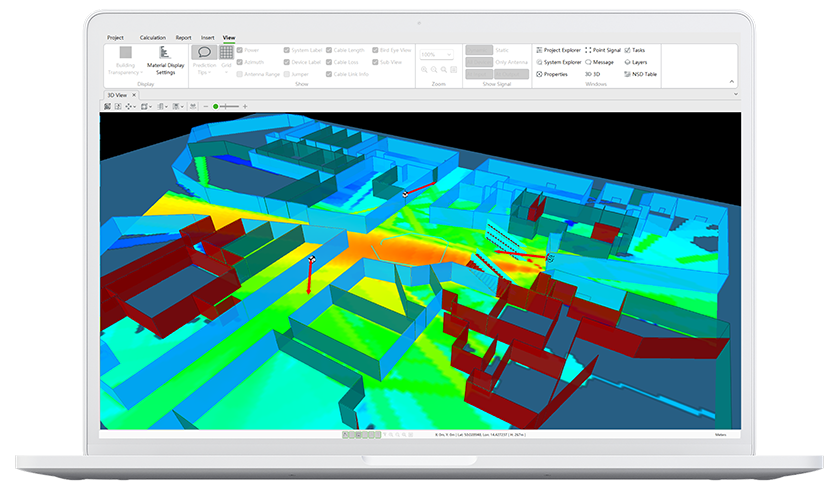
- The last-mile logistics scenarios are complex. Currently, there is no 3D true multiple-path ray-based radio propagation tool to predict how radio waves propagate in these scenarios, especially in the sub-Terahertz band identified for 6G.
- There lacks digital models of high-resolution last-mile logistics environment and 6G devices such as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS), and extremely large MIMO antenna arrays, which could be extremely useful for last-mile logistics use case.
- Radio access network (RAN) planning and optimization algorithms for last-mile logistics use cases are complex and computationally intensive, it is challenging to find fast and accurate algorithms to facilitate off-line network planning and online real-time network optimisation
Research Project - COMET

Technical Challenges

Implementation
To address the above challenges, COMET (Communications Enabled, AI/ML based Digital Twins for Smart city Logistics and Last Mile applications) project team has been assembled comprising world-class expertise in wireless communications, system modelling, performance analysis, software development, AI, and smart city related areas to address the above challenges and seize the large commercial opportunity.

Outcome
The success of the project will enable the provisioning of an innovative and comprehensive, digital twins-based solution for managing wireless infrastructure and the smart city last-mile logistics use case, enabled by 5G/6G communications. The project will contribute to the improvements in the digital economy and creating new jobs, which will have a huge impact in a wide range of vertical industries, e.g., smart living, and health care, etc. The project will also help strengthen the UK's position in the future wireless communications domains and smart city areas.
Research News
Explore our Research News
Discover how our cutting-edge research projects are shaping the future of wireless network technology